Network configuration
This section is an overview of how you deploy an ESXi gateway or a Hyper-V gateway within your network.
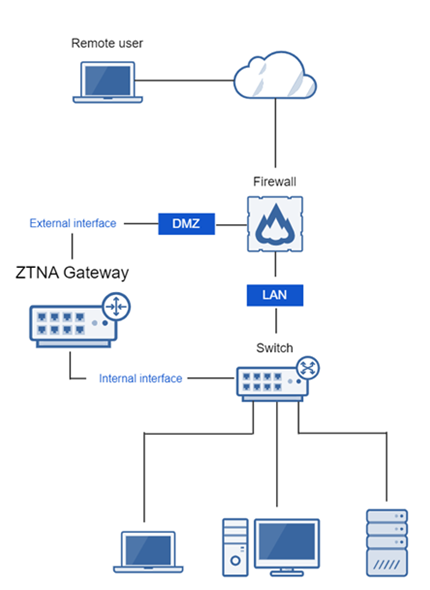
You can deploy an ESXi or Hyper-V gateway as a one-arm or two-arm proxy.
-
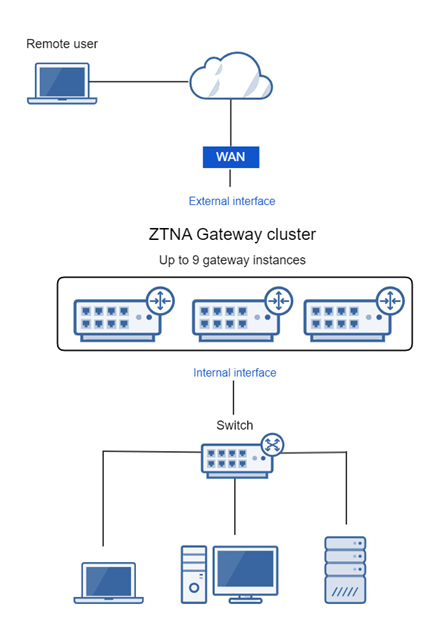
One-arm proxy deployment uses the WAN (external interface) for both incoming and outgoing traffic through the firewall. It minimizes changes to your infrastructure.
-
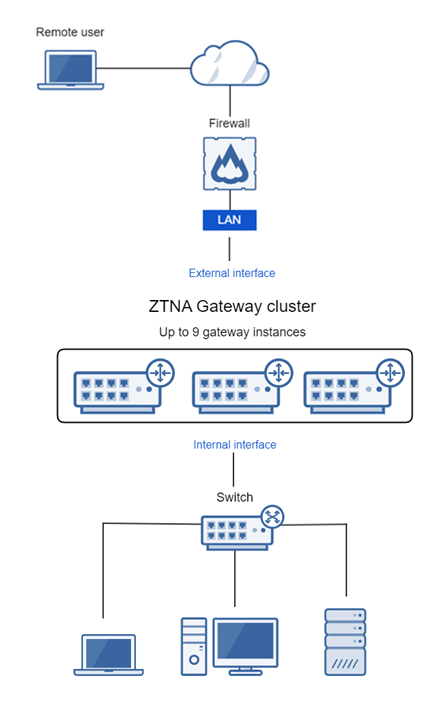
Two-arm proxy deployment uses both WAN and LAN (external and internal interfaces). This requires infrastructure changes but provides the best security and throughput.
When you set up an on-premises gateway, you must do as follows:
- Only open ports 80 and 443 (to allow inbound traffic) on the external interfaces of the gateway.
- Create a DNAT rule for ports 80 and 443.
- Block all other ports for security.
- Don't use reverse proxies.
When you set up a Sophos Cloud gateway, only open port 443 (to allow outbound traffic) on the external interfaces of the gateway.
You can choose whether the gateway connects to the firewall's LAN or DMZ, or (for two-arm) to the cloud.
Click on one of the tabs below to see the network configuration you can use for each deployment type.
Here are the configurations for one-arm deployments.
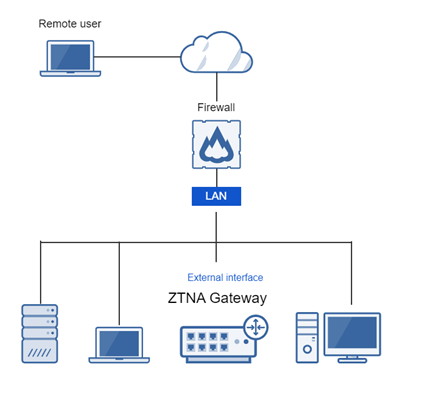
One-arm gateway connects to firewall LAN
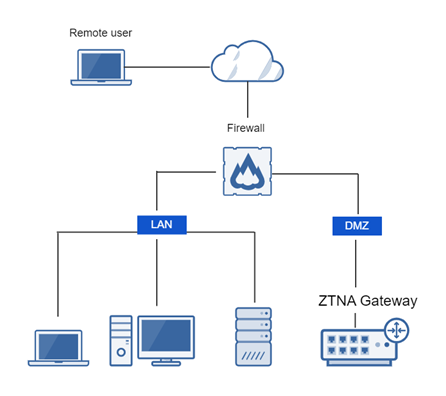
One-arm gateway connects to firewall DMZ