Set up Zero Trust Network Access
Sophos Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) lets you control access to resources (apps and web pages) on your network.
This guide includes instructions for third-party products. We recommend that you check the vendors' latest documentation.
You can watch the following video to learn how to set up ZTNA.
ZTNA deployment modes
You can deploy ZTNA with an on-premises gateway or a Sophos Cloud gateway based on your requirements. The deployment mode is interchangeable, and you can easily migrate from one gateway mode to another.
On-premises gateway
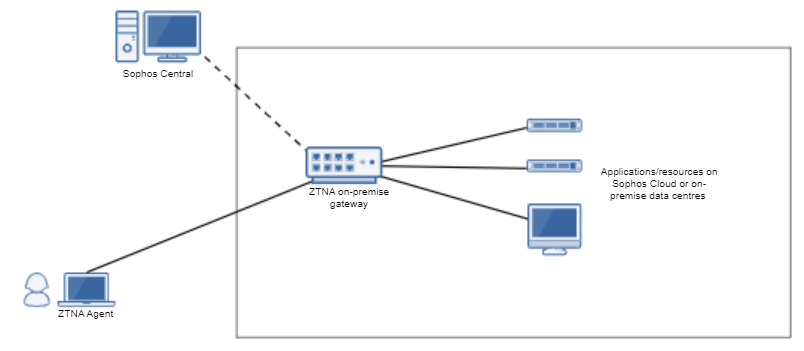
When you deploy an on-premises gateway, you set up gateways in your data centre.
You manage the gateways, which are exposed to the public internet, so you also need to open firewall ports and create NAT rules to manage your network.
Here's an example of on-premises gateway mode.
Sophos Cloud gateway
You can use a new Sophos-protected data-plane cloud to provide access to internal resources.
The multi-tenanted Sophos Cloud isolates network deployments from direct internet exposure and reduces the attack surface area. You can easily connect your users to applications without opening firewall ports and creating NAT rules.
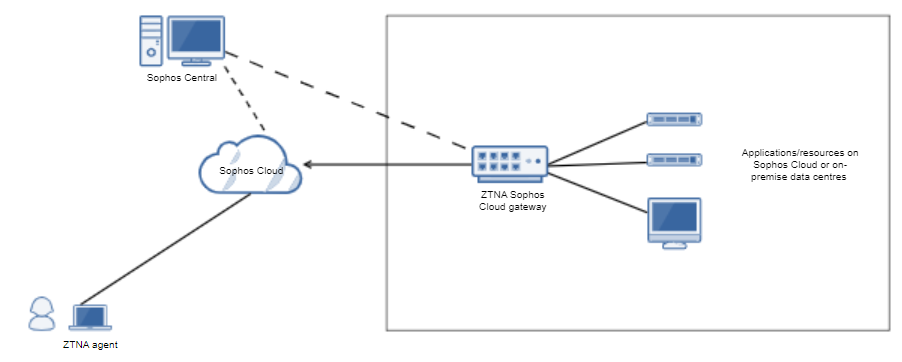
When a user attempts to access a resource, they're directed to Sophos Cloud. Sophos manages the data plane within Sophos Cloud. Your infrastructure is hidden from the internet. You set up gateways in your data centre to connect Sophos Cloud with your internal resources. You can choose from multiple points of presence to provide access to your internal resources. Choose the point of presence nearest to your datacenter to reduce latency.
Here's an example of Sophos Cloud gateway deployment mode.
Sophos Cloud deployment mode is delivered with availability of 99.999% except during any planned or emergency maintenance windows or due to issues caused by factors outside of Sophos's reasonable control. To see the availability of the points of presence and get notifications about upcoming maintenance, go to the Sophos status page. See Sophos status page.
The points of presence are as follows:
- Europe (Ireland) Region
- Europe (Frankfurt) Region
- US East (Ohio) Region
- US West (Oregon) Region
- Asia Pacific (Mumbai) Region
- Asia Pacific (Sydney) Region
On ZTNA 2.1 and later, a secondary point of presence is set up by default, nearest to your primary point of presence. There's automatic failover between the points of presence, so that users can access resources without any interruptions. Example: If you configure the Europe (Ireland) Region as the point of presence and the region goes down due to an outage, traffic is re-routed via the Europe (Frankfurt) Region until the original region comes up.
You can turn this off from the Settings page. See Sophos Central: Settings.
If there are any issues with a point of presence, you can change your point of presence to ensure that the potential impact on the user is minimal.
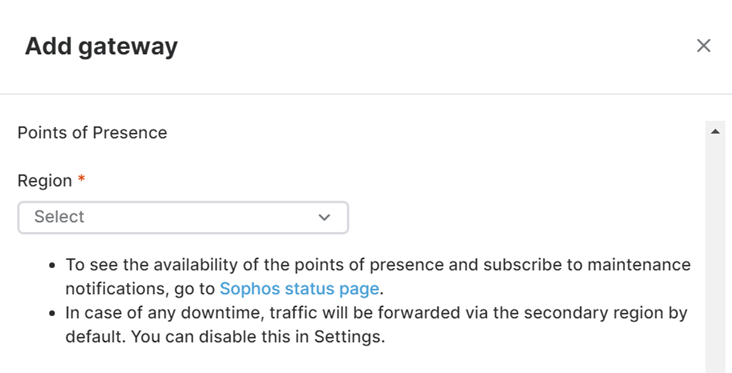
To change your point of presence, do as follows:
- Sign into Sophos Central.
- Go to My Products > ZTNA > Gateways.
- Click the gateway name.
- Click Edit.
- Under Points of presence select a region.
- Click Save.
Deployment information
To get information about on-premises gateways or Sophos Cloud gateways, click the tab for your deployment type below.
Sophos ZTNA consists of these components:
-
Sophos Central. This management tool lets you set up and manage a ZTNA on-premises gateway.
-
ZTNA on-premises gateway. A virtual appliance that authenticates users and authorizes them to access apps.
-
ZTNA agent. An agent installed on your devices. This lets ZTNA control local apps (not just web apps).
A ZTNA on-premises gateway is currently available for VMware ESXi and Hyper-V.
About setup
The main steps in setting up ZTNA are as follows:
- Check the requirements. See Requirements.
- Check the network deployments available. See Network configuration.
- Get a certificate. See Get a certificate.
- Set up a directory service. This manages your users. See Set up directory service.
- Synchronize users. This imports your users into Sophos Central. See Sync users in Sophos Central.
- Set up an identity provider (IDP). This authenticates users. See Set up an identity provider.
- Set up an on-premise gateway. This controls access to apps. See Set up an on-premises gateway.
- Add policies. These set conditions for access. See Add policies.
- Add your DNS settings. See Add your DNS settings.
- Install the ZTNA agent. This controls access to local apps. See Install the ZTNA agent.
- Add resources. This makes apps available and lets you specify which users can access them. See Add resources.
Sophos ZTNA consists of these components:
-
Sophos Central. This management tool lets you set up a gateway. The gateway is then managed by Sophos.
-
ZTNA Sophos Cloud gateway. A Sophos-protected data-plane cloud gateway that provides access to internal resources. This consists of Sophos Cloud and the gateway. You must deploy the gateway in data centers that host resources. These gateways connect Sophos Cloud and resources in your data center.
When you deploy your Sophos Cloud gateway, you configure your gateway's point of presence. To get the best latency and connectivity, choose a point of presence nearest to the datacenter in which you host your resources.
-
ZTNA agent. An agent installed on your devices. This lets ZTNA control local apps (not just web apps).
A ZTNA Sophos Cloud Gateway is currently available for VMware ESXi and Hyper-V.
About setup
The main steps in setting up ZTNA are as follows:
- Check the requirements. See Requirements.
- Get a certificate. See Get a certificate.
- Set up a directory service. This manages your users. See Set up directory service.
- Synchronize users. This imports your users into Sophos Central. See Sync users in Sophos Central.
- Set up an identity provider (IDP). This authenticates users. See Set up an identity provider.
- Set up a Sophos Cloud Gateway. This controls access to apps. See Set up a Sophos Cloud gateway.
- Add policies. These set conditions for access. See Add policies.
- Add your DNS settings. See Add your DNS settings.
- Install the ZTNA agent. This controls access to local apps. See Install the ZTNA agent.
- Add resources. This makes apps available and lets you specify which users can access them. See Add resources.