Add a bridge interface
You can set up a bridge interface over physical and virtual interfaces.
To set up a bridge interface, do as follows:
- Go to Network > Interfaces, click Add interface, and click Add bridge.
-
Enter a name. You can change this later.
Maximum number of characters: 58
The interface's customizable name rather than the hardware name is shown in other settings.
-
Enter a hardware name for the interface. You can't change this name later.
Maximum number of characters: 10
Allowed characters: (A-Za-z0-9_)
Restriction
The hardware name can't contain the following system-reserved names:
all,gre,oct,mv-pcimux0,mvmgmt0,pport_,lo,ipsec0,tun,ppp,imq,ifb,mast,sit,WWAN1,_ppp,vxlan,xfrm,USB,erspan0,Port,MGMT,eth,GE,gretap0,ip6tnl0,host,reds,wlnet,WLAN,Sophos,GuestAP,spq, andHalink.Restriction
You can't use bridge interfaces with Dynamic DNS, DHCP clients, PPPoE, and IPsec VPN.
-
Specify the settings.
Option Description Enable routing on this bridge pair Turn on routing on this bridge. If you've turned it on, you must assign an IP address to the bridge interface. Interface Interfaces on which you can set up a bridge:
- A physical interface, for example, Port1, PortA, or eth0.
- RED
- LAG
- VLAN interface on a physical interface, RED, or LAG
Zone Zone assigned to the interface. Member interfaces Interface and Zone of bridge members. You can select physical and VLAN interfaces.
To add more interfaces, select Add .
.Sophos Firewall drops traffic related to bridge interfaces without an IP address if the traffic matches a firewall rule with web proxy filtering or if it matches a NAT rule. These dropped packets aren't logged. To prevent NAT rules from causing the traffic to drop, do the following:
- Go to Rules and policies > NAT rules and select the SNAT rule to edit.
- Select Override source translation for specific outbound interfaces.
- Set Outbound interface to the bridge interface without IP address.
- Set Translated source (SNAT) to Original and click Save.
-
Specify the IPv4 or IPv6 configuration details. You must specify these settings if you selected routing on the bridge interface.
Option Description IP assignment Method of assigning the IP address. Select from the following options:
- Static
- DHCP
IPv4/netmask or IPv6/Prefix For static IP assignment, enter the IP address and select the netmask or prefix. Gateway name For bridge members with WAN ports, enter the gateway name. Gateway IP If you selected static IP assignment and bridge members with WAN ports, enter the gateway IP address. -
Specify the VLAN settings to forward or drop VLAN traffic passing through the bridge interface.
Name Description Filter VLANs Select to drop VLAN traffic passing through the bridge interface.
If you select filtering, but don't specify the permitted VLANs, Sophos Firewall drops tagged traffic from all the VLANs. Untagged traffic isn't dropped.
VLAN filtering applies only to bridged traffic. It won't apply to routed traffic.Permitted VLAN ID or ID range Enter VLAN IDs or ranges (example: 20-35).
Use this to forward traffic from the specified VLANs to the other bridge members. -
Specify the advanced settings: Use this to control broadcasts and traffic forwarded by the bridge interface.
Option Description Permit ARP broadcast By default, bridge interfaces forward ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) broadcasts to discover the destination MAC addresses.
Clear the check box to prevent ARP broadcasts. You can use this when there's a broadcast storm.
In the absence of ARP broadcasts, bridge interfaces can't create a bridge table with MAC addresses. To specify IP-MAC binding, go to Network and create static entries using Neighbors (ARP–NDP).Turn on Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Turn on STP to prevent bridge loops, which occur when there's more than one path between two bridge interfaces. Redundant paths can result in a broadcast storm in the network.
STP also enables failover to redundant paths dynamically when the primary path fails.
You can't turn on STP on any bridge interface when HA is enabled.STP max age Interval at which bridges transmit their configuration information. The default interval is 20 seconds.
Bridges send bridge protocol data units (BPDU) to transmit information, such as their interface, MAC address, port priority to other bridges at the STP max age interval. This enables them to update their tables with the network topology. BPDUs help detect failed paths in the network.MAC aging Interval at which inactive MAC addresses are removed from the bridge table. The default interval is 300 seconds.
Bridges record the timestamp of when they learn a MAC address. MAC addresses with timestamps older than the interval are removed.
In dynamic networks, such as guest Wi-Fi networks, you can use lower MAC aging intervals. In stable networks, such as networks with data centers, you can use higher intervals.MTU MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) value, in bytes. It's the largest packet size that a network can transmit. Packets larger than the specified value are divided into smaller packets before they are sent.If the MTU of the bridge interface and its members differs, the bridge interface inherits the lower value. To see the inherited MTU, go to the interface table.
Example:
Bridge MTU:9000
MTU of the interface used in VLAN (bridge member):1500
Inherited bridge MTU becomes1500.Override MSS Select to override the MSS value.
MTU is the sum of the TCP and IP header values and the payload value. When additional packet encapsulation takes place, for example in IPsec tunnels, the packet size can become larger than the defined MTU value, leading to dropped packets or additional fragmentation.
Overriding the specified MSS value ensures that the packet size stays within the defined MTU value.MSS MSS (Maximum Segment Size), in bytes. It's the amount of data that can be transmitted in a TCP packet. Filter Ethernet frames The default setting allows all Ethernet frames to pass through the bridge.
Select to drop Ethernet frames from passing through the bridge. The drop setting doesn't affect the frames of ARP, IPv4, IPv6, 8021Q, EXTE traffic, which are always allowed.
If you select filtering, but don't specify the permitted Ethernet frame types, Sophos Firewall drops traffic for all Ethernet frames except the frames that are always allowed.Forwarded Ethernet frame types Specify the EtherTypes whose Ethernet frames you want to forward through the bridge interface. Enter the four-digit hexadecimal ID of the EtherType.
Example: AppleTalk (809B), Novell (8138), PPPoE (8863 and 8864)To update the log viewer with dropped packet details, go to System services > Log settings. Under Firewall, select Bridge ACLs.
To see the logs, go to Log viewer and select Add filter. Set the field to Log component and Value to Bridge ACLs.
Additionally, you can set the field to Log subtype and value to ARP broadcasts, EtherType filtering, or VLAN filtering.
-
Click Save.
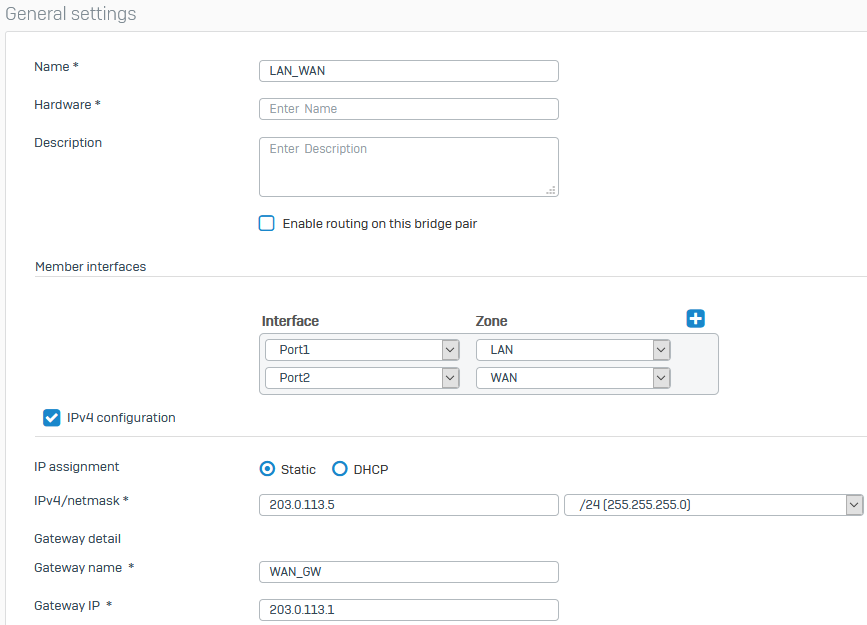
The following image shows example bridge settings: