IPsec connections
You can configure IPsec VPN connections to allow cryptographically secure communication over the public network between two Sophos Firewall devices or between Sophos Firewall and third-party firewalls.
You can configure the following types of IPsec VPNs:
- Route-based VPNs
- Policy-based VPNs
You can manage IPsec connections using failover groups.
IPsec profiles
IPsec profiles specify the encryption and authentication algorithms and key exchange mechanisms for policy-based and route-based IPsec connections. In IPsec profiles, you define the phase 1 and phase 2 security parameters, and assign a profile to IPsec connections.
To configure IPsec profiles, go to Profiles > IPsec profiles.
Sophos Firewall establishes IPsec connections based on matching IPsec profiles configured at the connection's local and remote ends.
IPsec connections
You can configure policy-based (host-to-host and site-to-site) and route-based (tunnel interface) IPsec connections.
You can do the following:
- Click IPsec profiles to edit or create a profile. You can specify the phase 1 and phase 2 IKE (Internet Key Exchange) parameters for establishing IPsec and L2TP tunnels.
- Click Logs to see the logs.
-
Click Show additional properties above the name column to select additional settings for the list view. You can drag and drop the properties to rearrange the list view.
Tip
You may need the IPsec connection's properties to troubleshoot IPsec tunnels and failover groups.
Policy-based connections
You must configure policy-based IPsec connections (Site-to-site and Host-to-host) and the corresponding firewall rules on both networks.
You can configure these manually, or click Wizard and allow the assistant to help you specify the settings for policy-based VPNs. You can't edit connections using the assistant.
Network address translation: If the local and remote subnets overlap, you must specify the NAT settings in the IPsec configuration.
Route-based connections
You can configure route-based VPNs by setting Connection type to Tunnel interface. See route-based connections. You must configure the corresponding firewall rules.
Currently, you can't create route-based connections using the assistant. When you configure a route-based IPsec connection, Sophos Firewall automatically creates an XFRM interface, also called a virtual tunnel interface (VTI). The interface is shown as xfrm followed by a number on Network > Interfaces.
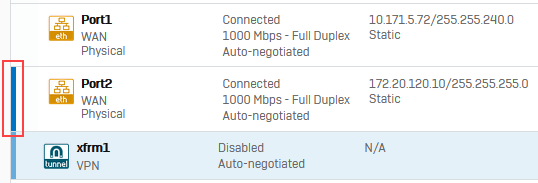
Note
Physical interfaces with a virtual interface assigned to them, for example XFRM or VLAN interfaces, have a blue bar on the left. To see the XFRM interface, click the listening interface you've used to configure the route-based IPsec connection. The XFRM interface then appears under this interface.
You must assign an IP address to XFRM interfaces configured using Any for the local and remote subnets or IP version set to Dual. You must configure static, SD-WAN, or dynamic routes to determine the traffic to be sent to the XFRM interface. SD-WAN routes allow you to apply Service Level Agreements (SLAs) for the traffic through the assigned SD-WAN profiles.
Network address translation: If the local and remote subnets overlap, you must do as follows:
- If you've selected Any for the local and remote subnets, you must configure the corresponding SNAT and DNAT rules (Rules and policies > NAT rules).
- If you've selected specific local and remote subnets, you must configure the NAT settings in the IPsec configuration.
Tip
By default, MASQ in an SNAT rule translates the original IP address to the WAN IP address.
However, for route-based VPNs configured with Any for the local and remote subnets or IP version set to Dual, the firewall translates the original source to the XFRM IP address for the translated source set to MASQ.
You can see the XFRM IP address in TCP dump and packet capture. The IP addresses are shown as follows:
WAN IP address: On the outer IP header of the encapsulated packet.
XFRM IP address: On the inner IP header for the source.
Warning
If traffic related to route-based VPNs with traffic selectors matches a masqueraded SNAT rule, the firewall drops the traffic because IP addresses aren't assigned to these XFRM interfaces.
IPsec routes
Sophos Firewall creates IPsec routes automatically when policy-based IPsec tunnels are established. However, you must add IPsec routes for some traffic manually. Some examples are as follows:
- You want to route system-generated traffic, such as authentication requests, from a remote office to the head office through an IPsec connection. See Route system-generated authentication queries through an IPsec tunnel.
-
You can't add some subnets to the IPsec connection for internal reasons. However, you want their traffic to flow through the connection.
Note
If a static or SD-WAN route applies to the remote subnets specified in a policy-based IPsec connection, make sure you set the route precedence to VPN route before static or SD-WAN route. You can do this on the CLI. See the following example: system route_precedence set vpn static sdwan_policyroute
See SD-WAN routes.
Connection status
Connection statuses are of the following two types:
- Active (active-inactive status): To activate a connection, you can click Activate on save during the configuration. Alternatively, you can click the Active status
 for the connection from the list of configured connections.
for the connection from the list of configured connections. - Connection (established-not established): To establish a connection, you can click Connection status
 for the connection from the list of configured connections.
for the connection from the list of configured connections.
| Active | Connection | Description |
|---|---|---|
 |  | Connection is active, but tunnel isn't established. |
 |  | Connection is active, and tunnels are established. |
 |  | Connection is active, but at least one tunnel isn't established. When you configure more than one local or remote subnet, Sophos Firewall establishes a tunnel for each local and remote subnet pair. |
 |  | Connection is inactive. |
Failover group
A failover group is a sequence of IPsec connections. If the primary connection fails, the next active connection in the group automatically takes over.
- To activate a group and establish the primary connection, click Status
 .
. - To troubleshoot IPsec tunnels in a failover group, see Troubleshoot IPsec VPN and failover groups.
- Turning off a failover group deactivates the active tunnels belonging to the group. You must activate these tunnels individually if required.
Automatic failback
Sophos Firewall checks the remote gateway's health based on the failover condition you specify for the group. It performs the health check at the interval you specify for Gateway failover time-out on Network > WAN link manager.
Sophos Firewall tries to restore the primary IPsec connection when the remote gateway is live again. If it's unable to restore it, it continues to use the secondary connection and won't check the primary connection again for automatic failback. It will only fail back to the primary if the secondary connection's remote gateway goes down. To restore the primary connection manually, go to the failover group list and click the status button off, then on again for the group. This involves downtime.
When the failover group contains more than two IPsec connections, Sophos Firewall fails back to the first available connection in the group's Member connections.
More resources