Block internet access based on MAC address
MAC address filtering is more secure than IP address filtering because MAC addresses rarely change. The IP addresses of hosts change in a DHCP environment, so filtering MAC addresses is more reliable for identifying and filtering the source and destination of network traffic.
MAC address filtering is the most common security measure to prevent unwanted network access in a wireless network environment. The firewall is configured to only accept traffic from specific MAC addresses, and the allowed devices will get new IP addresses through DHCP. This means that devices can still communicate with the network. Any attempt to communicate by masquerading the IP address is blocked since the MAC address won't match the allowed MAC addresses.
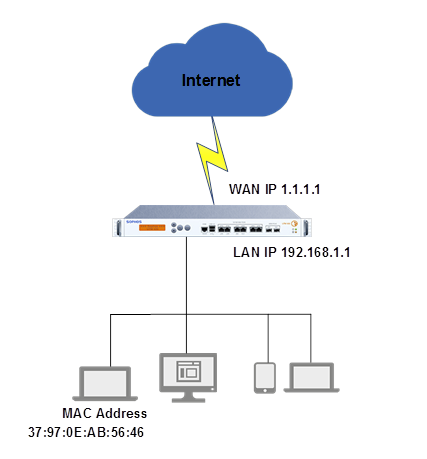
This example blocks the IPv4 traffic from the LAN to the WAN for the MAC host 37:97:0E:AB:56:46.
Network diagram
Create a MAC host
- Go to Hosts and services > MAC host, and click Add.
-
Configure the following settings:
Setting Value Name MAC_HostType MAC address MAC address 37:97:0E:AB:56:46 -
Click Save.
Create a firewall rule
- Go to Rules and policies > Firewall rules, click Add firewall rule, then click New firewall rule.
-
Configure the following settings:
Setting Value Rule name Block_MACAction Drop Log firewall traffic Selected Rule position Top Rule group None Source zones LAN Source networks and devices MAC_HostDuring scheduled time All the time Destination zones WAN Destination networks Any Services Any -
Click Save.
Note
MAC-based internet filtering only works when the devices are directly connected to the firewall. Turn on MAC binding in network scenarios where the devices are connected via a firewall, router, or a layer three switch. See Add a user locally.