Create a source NAT rule
This example shows how to create a source NAT rule to translate outgoing traffic from the LAN zone.
Objectives
When you complete this unit, you'll know how to do the following:
- Create a source NAT rule to translated outgoing traffic from the LAN.
- Create a firewall rule to allow outgoing traffic from LAN to WAN zone.
SNAT network diagram
Source NAT is typically used to translate outgoing traffic from the internal network to external resources on the internet. The source IP address is translated, keeping it private. The following network information is illustrative:
- Pre-NAT IP address of LAN users:
10.145.16.10/24 - Post-NAT IP address of LAN users:
MASQ(IP address of the applicable outbound interface)

Here's an example:
- Source NAT from the internal network to WAN:
Network LAN(10.145.16.0/24) toAny - Firewall rule to allow traffic from LAN zone to WAN:
LANtoAny
Specify the NAT rule settings
- Go to Rules and policies > NAT rules, select IPv4 or IPv6 and click Add NAT rule.
- Specify the rule name and rule position.
-
Select the translation settings for outgoing traffic.
Name Description Original source Network_LANTranslated source (SNAT) MASQOriginal destination AnyTranslated destination (DNAT) OriginalOriginal service AnyTranslated service (PAT) OriginalInbound interface Port3Outbound interface Port1 -
Click Save.
The following image shows an example of how to configure the settings:
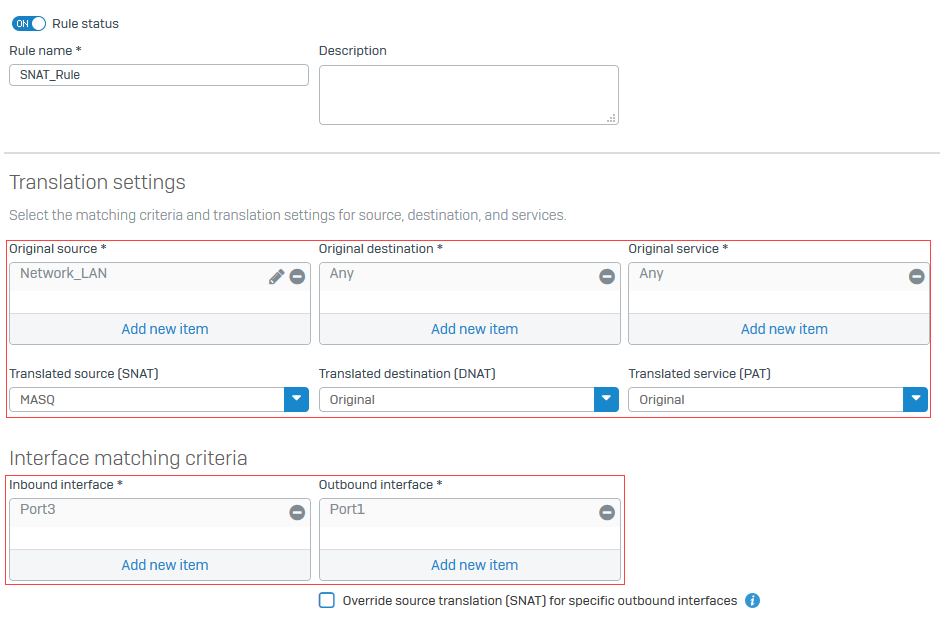
Create a firewall rule to allow traffic that matches the source NAT rule.
Specify firewall rule settings for SNAT traffic
- Go to Rules and policies > Firewall rules. Select protocol IPv4 or IPv6 and select Add firewall rule. Select New firewall rule.
- Specify the rule name and rule position.
-
Specify the source, destination, and services as follows:
Name Description Source zones LANSource networks and devices Network LANDestination zones WANDestination networks AnyServices Any -
Specify the security settings and click Save.
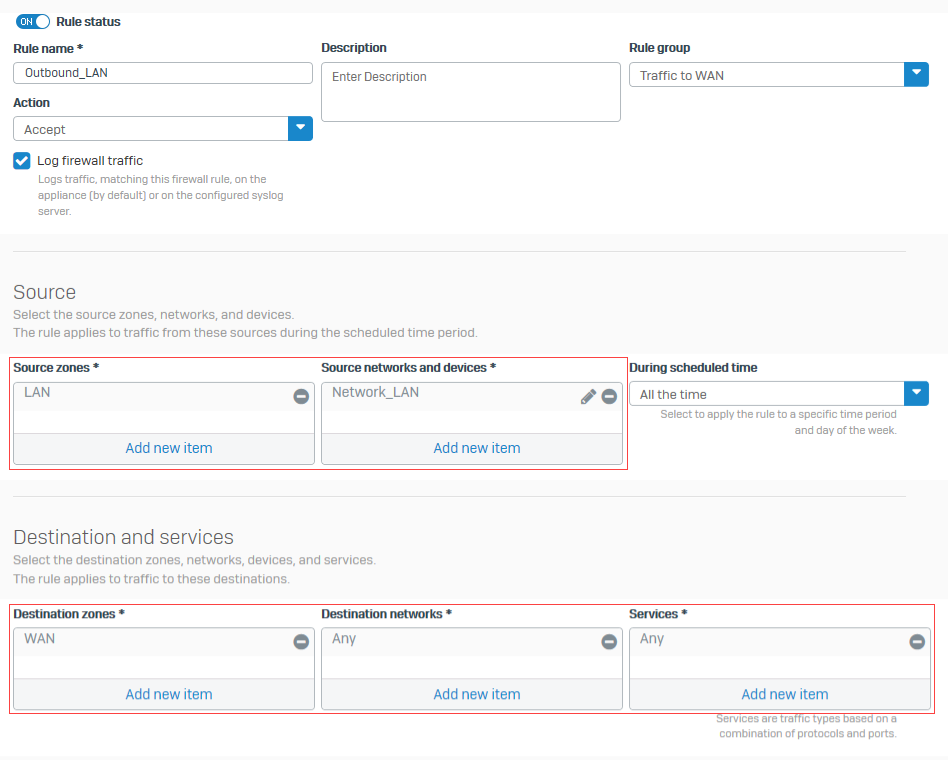
You created a firewall rule to allow traffic from the LAN zone to external networks.
More resources