Troubleshoot IPsec VPN and failover groups
To troubleshoot site-to-site IPsec VPN connections and failover groups, you can check the logs, IPsec profiles, and connection properties.
Check logs and configurations
Logs
The firewall uses the following files in /log to trace the IPsec events:
strongswan.log: IPsec VPN service logcharon.log: IPsec VPN charon (IKE daemon) logstrongswan-monitor.log: IPsec daemon monitoring logdgd.log: Dead Gateway Detection (DGD) and VPN failover log
This page helps with troubleshooting errors that relate to this error message: IPsec connection could not be established
Open the following log file: /log/strongswan.log
IPsec connections
To troubleshoot a failover group, see the additional properties of the group's IPsec connections and their IPsec profiles.
- To see the additional properties of IPsec connections, go to Site-to-site VPN > IPsec.
-
Under IPsec connections, click Show additional properties above the name column and select the properties you want to see in the IPsec connection list.
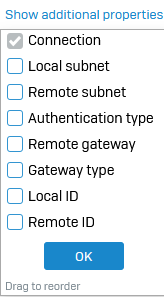
IPsec profiles
- To see the additional properties of the IPsec profile used in a connection, go to Profiles > IPsec profiles.
-
Click Show additional properties above the name column and select the additional properties you want to see.

Troubleshoot IPsec connections and failover groups
See the following issues and their resolution.
Remote peer refuses Phase 1 proposal
The strongSwan log shows the following error message: Remote peer is refusing our Phase 1 proposals
Cause: Mismatched phase 1 proposals between the two peers.
-
Make sure the VPN configuration on both firewalls has the same settings for the following:
- Phase 1: Encryption, authentication, and DH group.
- Gateway address: The peer gateway address you've entered on the local firewall matches the listening interface in the remote configuration.
- Other settings: Local and remote IDs.
-
If all the settings match, the remote firewall administrator must check the configuration at their end since the remote firewall has refused the connection.
Remote peer doesn't authenticate
The strongSwan log shows the following messages:
We have successfully exchanged Encryption and Authentication algorithms, we are now negotiating the Phase 1 SA encryption (hashing) key
Remote peer reports we failed to authenticate
Cause: The remote firewall couldn't authenticate the local request because the ID types don't match. Example: You've configured the local firewall's IPsec connection with Local ID set to IP address, but the remote firewall is configured to expect a DNS name.
- Check the logs on the remote firewall to make sure the mismatch of ID types has resulted in the error.
- Update the local and remote ID types and IDs with matching values on both firewalls.
Decryption error
Logs show the following error messages:
Error on decryption of the exchange
Information field of the IKE request is malformed or not readable
Cause: The cause is likely to be a preshared key mismatch between the two firewalls.
Rarely, the ISP or an upstream appliance, such as a router or another firewall, may corrupt the packet.
- Make sure the preshared key matches in the VPN configuration on both firewalls.
- If the preshared key matches, verify with the ISP or on the upstream devices if they've corrupted the packet.
- Make sure the WAN interface's MTU and MSS settings match the values given by the ISP.
Remote peer reports no match on the acceptable proposals
The strongSwan log shows the following messages:
Phase 1 is up
Initiating establishment of Phase 2 SA
Remote peer reports no match on the acceptable proposals
The remote firewall shows the following error message: NO_PROPOSAL_CHOSEN
Cause: Mismatched phase 2 proposal.
- Make sure the phase 2 settings for encryption and authentication algorithms and DH group match on both firewalls.
- If they match, check the remote firewall logs for the cause.
Invalid ID
The strongSwan log shows the following messages:
Phase 1 is up
Remote peer reports INVALID_ID_INFORMATION
Cause:
- Sign in to the CLI and click 5 for Device management and then click 3 for Advanced shell.
-
Enter the following command:
ipsec statusallYou can see that the SA (Security Association) isn't shown. See the following image:
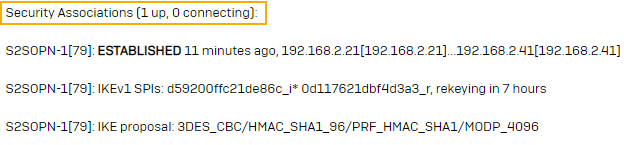
-
Enter the following command:
ip xfrm policyThe output doesn't show the phase 2 SAs. During the phase 2 negotiation, the local and remote subnets specified on the firewalls didn't match. For example, the remote firewall expects 192.168.0.0/24, but the local firewall tries to negotiate using 192.168.1.0/24.
-
Make sure the configured subnets match on both firewalls.
- If the subnets match, the remote administrator must check the remote firewall's logs if the error persists.
IPsec connections established but traffic stops later
One or more IPsec connections are established between Sophos Firewall and a third-party firewall. Traffic stops flowing after some time.
- Sign in to the CLI console. See Accessing Command Line Console.
- Type
5to selectDevice Management, then type3to selectAdvanced Shell. -
Enter the following command:
ipsec statusallThe output shows that IPSec SAs have been established.
-
Optional: For route-based VPN, enter the following command:
ip xfrm stateThe output shows the transform sets for the VPN exist, that is, the SAs match.
-
Check one or more of the following possible causes and resolutions:
Cause: Third-party remote firewall uses traffic-based rekeying.
Resolution: Sophos Firewall only supports time-based rekeying. If you've configured traffic-based rekeying on the third-party remote firewall, change it to time-based rekeying.
Cause: Two or more IPsec connections have the same local and remote subnets (including Any-Any configurations) but aren't in the same failover group.
Resolution: Multiple IPsec connections with the same local and remote subnets (including Any-Any configurations) only work if the IPsec connections are in the same failover group. To resolve this issue, do as follows:
- Go to Site-to-site VPN > IPsec.
- Under IPsec connections, click Show additional properties.
- Select Local subnet and Remote subnet.
-
Click OK.
The Local subnet and Remote subnet columns appear. Check the IPsec connections that have similar local and remote subnet configurations.
Example:
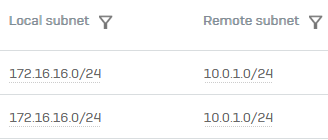
-
Configure the IPsec connections with similar local and remote subnets configurations in the same failover group. See Add a failover group.
- If you don't want to configure them in the same failover group, you must change those IPsec connections' local and remote subnet configurations and make sure they aren't similar.
Cause: For route-based VPN, two or more XFRM interfaces are configured with an IP address that belongs to the same network address or have overlapping subnets.
Resolution: Each XFRM interface must be in a unique network address and can't have overlapping subnets.
For example, if
xfrm1is configured with192.168.0.1/24andxfrm2is configured with192.168.0.6/24, they're in the same network address, so a routing issue occurs. Another example is ifxfrm1is configured with192.168.0.1/16andxfrm2is configured with192.168.0.6/24, the subnets overlap, so a routing issue occurs.To resolve this issue, go to Network > Interfaces and change the IP address configuration of the XFRM interfaces that are in the same network or have overlapping subnets. See Edit the xfrm interface (HO).
Cause: For policy-based VPN, the idle timeout is set on the remote firewall.
Resolution: Turn off the idle timeout on the remote firewall.
Cause: Key exchange collisions.
Resolution: To prevent key exchange collisions, do as follows:
- Set the initiator's phase 1 and phase 2 key life values lower than the responder's.
-
Set the phase 2 key life lower than the phase 1 value in both firewalls.
Example:
Key life Firewall 1 Firewall 2 Phase 1 12600 seconds 10800 seconds Phase 2 5400 seconds 3600 seconds
IPsec connection is disconnected because the associated interface is turned off
If your site-to-site IPsec connection is disconnected, check if you have turned off the associated interface.
If you've turned off the associated interface:
- Site-to-site IPsec connection initiators immediately disconnect the connection.
- Site-to-site IPsec connection responders and remote access connections disconnect the connection when inactivity or Dead Peer Detection (DPD) time-out occurs.