Configure BGP MED
You can configure the preferred entry path in BGP using the MED (Multi-Exit Discriminator) attribute when an Autonomous System (AS) has more than one entry path.
MED values are propagated to routers in the neighbor AS.
When is MED used
MED is an external attribute that's used when two neighbor AS' have multiple links between them, and the origin AS prefers one link over the others.
By default, routers evaluate MED when they learn two or more routes from the same AS to the same prefix, that is, the destination network. You can change this behavior. Based on MED, they select the entry router into the original AS.
MED is a non-transitive attribute and isn't forwarded to other neighbors. When the receiving AS forwards the route to a different AS, MED is reset to 0.
BGP evaluates MED after it evaluates weight, local preference, the locally originated attribute, the AS path length, and the origin type to reach an AS. It evaluates MED to select the route if all these attributes are equal.
Example scenario
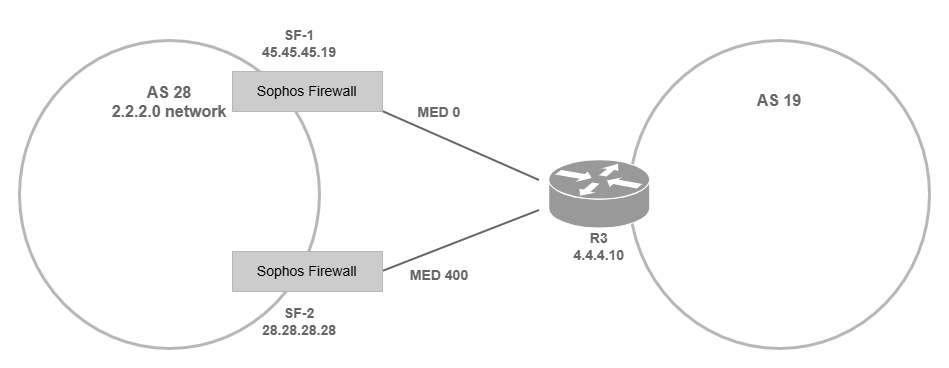
The following example shows how to configure MED so that the router in AS 19 prefers SF-1 for entry into the AS 28 network.
You must use your actual network and neighbor addresses and router IDs based on your network topology. The example uses the following values:
-
AS with two Sophos Firewall devices:
28- Network address of AS 28:
2.2.2.0 -
Preferred firewall (SF-1):
- IP address:
45.45.45.19 - MED value (metric):
0
- IP address:
-
Second firewall (SF-2)
- IP address:
28.28.28.28 - MED value (metric):
400 - Route map's name:
testroute
- IP address:
- Network address of AS 28:
-
Neighbor AS:
19- Router:
R3
- Router:
Key concepts
- The default MED value is 0.
- A lower MED value has higher preference. So, you assign a higher value to the route you don't prefer.
- To assign a value to MED, use the
metriccommand underroute-map.
Configure MED
You can configure the MED using the CLI as follows:
- Configure a route map with the MED value.
- Associate the route map with a neighbor.
Note
You can also use the route map to configure other BGP attributes, such as weight and community.
Configure a route map
You must change the MED value in SF-2 so that neighbors give a lower preference to it.
-
To enter the BGP configuration mode, enter the following options:
- For Route configuration: 3
- For Configure unicast routing: 1
- For Configure BGP: 3.
-
Run the following commands:
- Enter the global configuration mode:
conf torconf terminal -
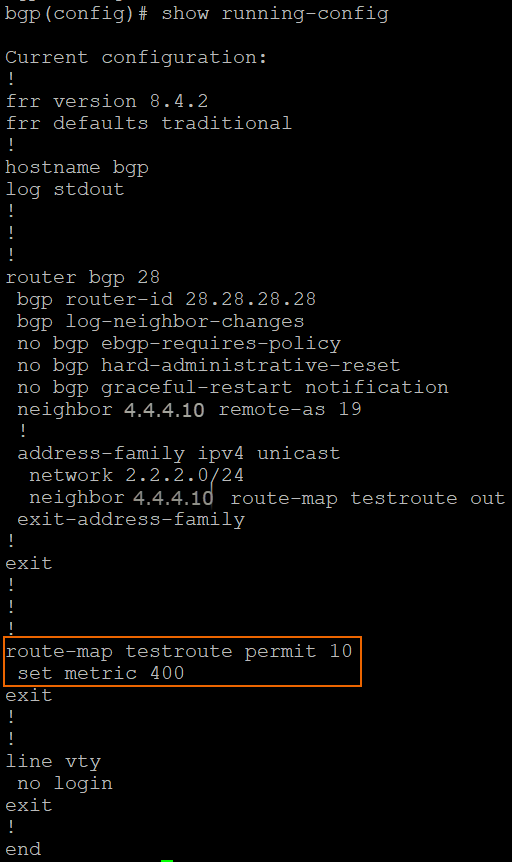
Create the route map entry:
route-map <route map's name> permit <sequence number>The firewall reads the route maps in the order they're listed. The sequence number determines the order. If you don't enter a sequence number, the most recent entry is listed at the top of the routing table.
-
Set the metric:
set metric <value>Example
bgp# conf t bgp(config)# route-map testroute permit 10 bgp(config-route-map)# set metric 400 bgp(config-route-map)# exit bgp(config)# sh run
- Enter the global configuration mode:
Associate the route map with a neighbor
-
To associate the route map with the neighbor, run the following commands:
- Enter the BGP configuration:
router bgp - Enter the IPv4 address family mode:
address-family ipv4 unicast - Associate the route map with the neighbor:
neighbor <ip address> route-map <route map's name> out - Save all the configurations you've made in this example:
write -
End the configuration:
endExample
bgp(config)# router bgp bgp(config-router)# address-family ipv4 unicast bgp(config-router-af)# neighbor 45.45.45.19 route-map testroute out bgp(config-router-af)# write bgp(config-router-af)# end
- Enter the BGP configuration:
-
To see the BGP configuration:
show running-config -
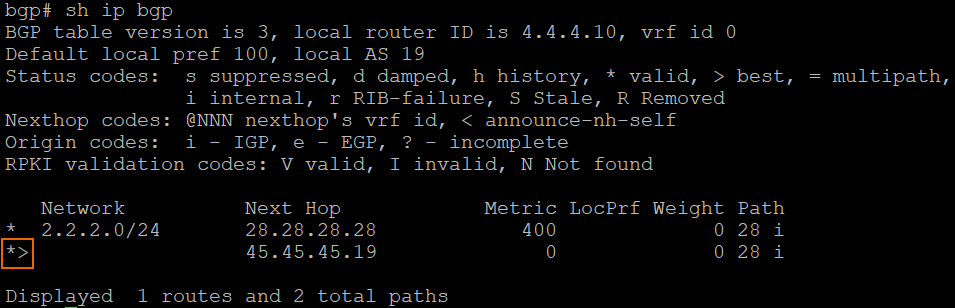
To verify the preferred route in the neighbor's routing table, run the following command:
sh ip bgpThe angle icon indicates the preferred route to the network.
Note
If Sophos Firewall is the neighbor, you can also see the routing table on the web admin console on Routing > Information. Under BGP-IPv4, click Routing.