Add a link aggregation group
To add a link aggregation group (LAG), do as follows:
- Go to Network > Interfaces, click Add interface and select Add LAG.
-
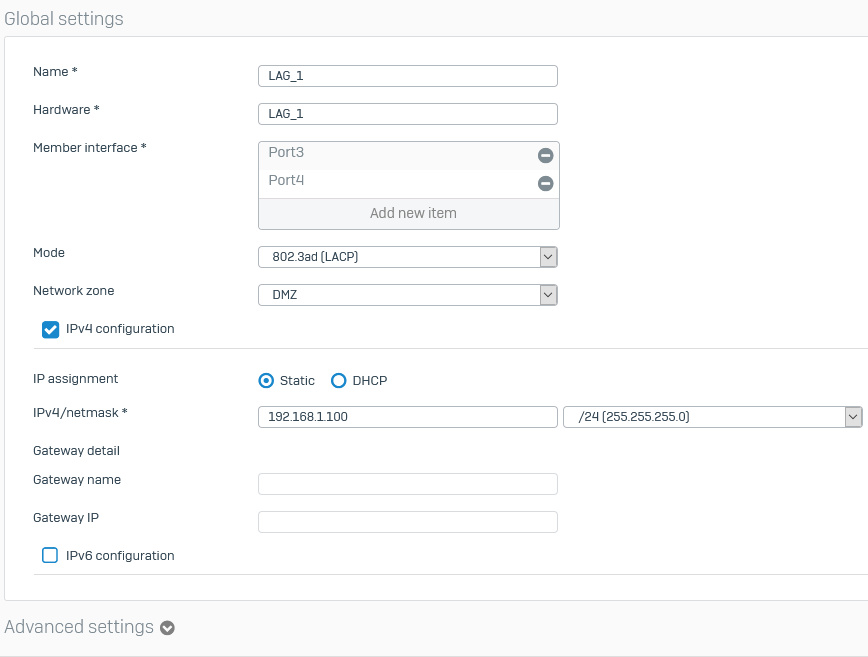
Enter a name. You can change this later.
Maximum number of characters: 58
The interface's customizable name rather than the hardware name is shown in other settings.
-
Enter a hardware name for the interface. You can't change this name later.
Maximum number of characters: 10
Allowed characters: (A-Za-z0-9_)
Restriction
The hardware name can't contain the following system-reserved names:
all,gre,oct,mv-pcimux0,mvmgmt0,pport_,lo,ipsec0,tun,ppp,imq,ifb,mast,sit,WWAN1,_ppp,vxlan,xfrm,USB,erspan0,Port,MGMT,eth,GE,gretap0,ip6tnl0,host,reds,wlnet,WLAN,Sophos,GuestAP,spq, andHalink. -
Under Member interface, click Add new item and select two to four interfaces.
Note
Only unbound static physical interfaces can be members of the LAG. Interfaces that you configure for PPPoE, cellular WAN, or WLAN can't participate in the LAG.
-
Select a mode.
Setting Description Active–Backup This mode provides link failover. One member link remains active while the others remain in standby mode. When the active link fails, the standby link becomes active. 802.3ad (LACP) This mode provides failover and load balancing. In this mode, traffic is distributed among all links. Observe the following requirements:
- LACP must be enabled at both ends of the link.
- All of the member interfaces must be of the same type and have the same interface speed.
- All links must be full-duplex.
-
Select a network zone.
-
Specify the IPv4 or IPv6 configuration details.
Setting Description IP assignment Method of assigning the IP address. Select from the following options:
- Static
- DHCP
IPv4/netmask or IPv6/Prefix For static IP assignment, enter the IP address and select the netmask or prefix. Gateway name For bridge members with WAN ports, enter the gateway name. Gateway IP If you selected static IP assignment and bridge members with WAN ports, enter the gateway IP address. The image below shows global settings.
-
Under Advanced settings, specify the Port settings:
Setting Description Link mode Interface speed and duplex for synchronization. Select a mode from the list.
The options shown depend on the appliance model.
Note: Speed mismatch between the device and third-party routers and switches may result in errors or collisions, disconnection, increased latency, or slow performance.
Auto-negotiation for media type Auto-negotiation of speed and duplex. Turn it on or off. Forward Error Correction (FEC) FEC mode of the interface. Select a mode from the list.
The options shown depend on the appliance model.
To use the recommended settings, click Show recommended settings and then click Load recommended configuration.
-
Under Advanced settings, specify the Interface settings:
Setting Description MTU MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) value, in bytes. It's the largest packet size that a network can transmit. Packets larger than the specified value are divided into smaller packets before they are sent.
Note: When networks with differing MTU sizes are interconnected, packets larger than the specified MTU value are fragmented before they're sent.Override MSS The maximum segment size is the largest amount of data, in bytes, that a device can receive in a single TCP segment. Xmit hash policy For LAGs that use 802.3ad (LACP) mode, assign load sharing across links based on the algorithm applied in the xmit hash policy. - Layer2: Generate the hash value using MAC addresses.
- Layer2+3: Generate the hash value using a combination of layer 2 (MAC address) and layer 3 (IP address) protocol information.
- Layer3+4: Generate the hash value using transport layer protocol information.
Use default MAC address Use the default MAC address of the interface. By default, the first port included as a member port becomes the default MAC address. Override default MAC address Override the default MAC address of the interface and enter a new address. On factory reset, the address is reset to the default MAC address. -
Click Save.
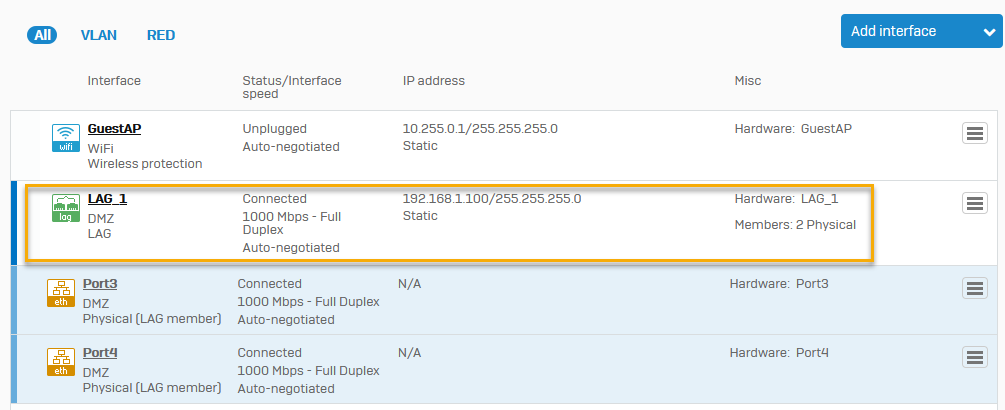
You can see the new LAG under Interfaces.