Configure a route-based VPN failover with two ISP connections
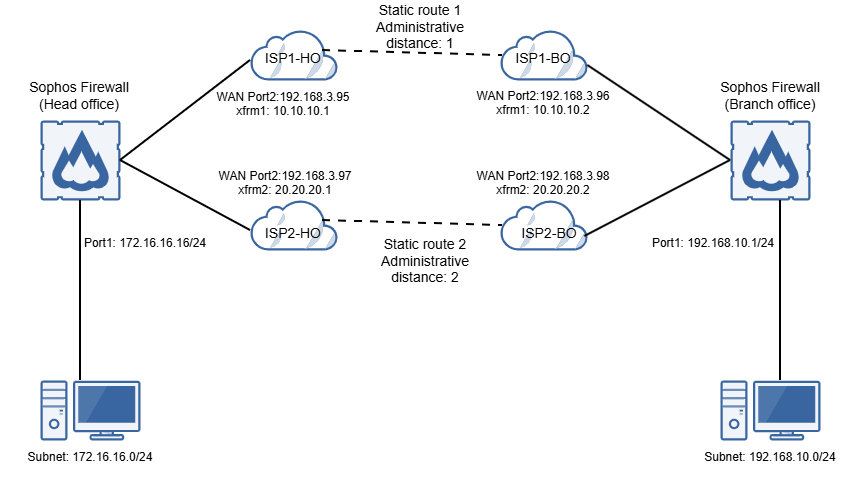
You can configure failover between route-based VPNs created over two different Internet Service Providers (ISPs). For example, you can create route-based VPN tunnels between your head office (HO) and branch office (BO) firewalls for ISP1 and ISP2. If ISP1 goes down, the traffic fails over to ISP2. When ISP1 recovers, the traffic fails back to ISP1.
Key steps
The key steps are as follows:
-
Configure the HO firewall as follows:
- Configure the route-based VPN connections.
- Assign IP addresses to XFRM interfaces.
- Add gateway hosts.
- Add static routes.
- Set the route precedence.
-
Configure the BO firewall as follows:
- Configure the route-based VPN connections.
- Assign IP addresses to XFRM interfaces.
- Add gateway hosts.
- Add static routes.
- Set the route precedence.
All configuration details are examples based on the network in the following diagram:
Head office firewall
Configure the route-based VPN connections
To configure the route-based VPN connections, do as follows on your HO firewall:
-
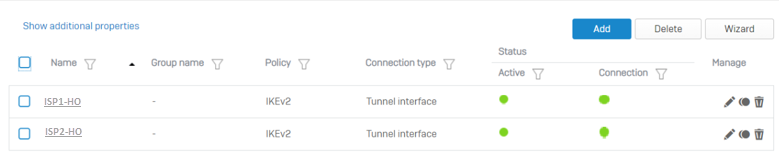
Create a route-based VPN tunnel between your HO and BO firewalls for ISP1.
-
Create a route-based VPN tunnel between your HO and BO firewalls for ISP2.
For instructions on how to create a route-based VPN tunnel, see Create a route-based VPN (any to any subnets).
To see your configured VPN connections, go to Site-to-site VPN > IPsec.
Assign IP addresses to XFRM interfaces
You must assign an IP address to each XFRM interface, as follows:
-
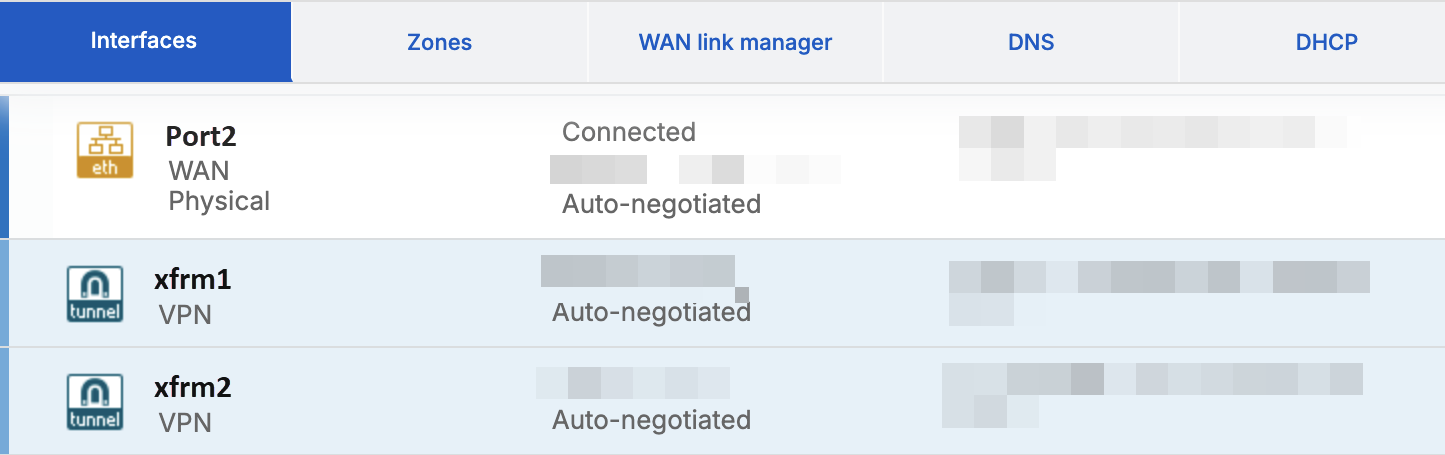
Go to Network > Interfaces and expand the WAN interface used to create the IPsec connection.
XFRM interfaces are automatically created for the tunnels. For example, you can see that the xfrm1 and xfrm2 interfaces are created under the WAN interface.
-
Assign an IP address to each XFRM interface.
Note
The settings we use below are examples.
- Click the xfrm1 interface.
- For IPv4/netmask, enter
10.10.10.1and/24(255.255.255.0). - Click the xfrm2 interface.
- For IPv4/netmask, enter
20.20.20.1and/24(255.255.255.0).
Add gateway hosts
Add a gateway host for each XFRM interface.
-
Add a gateway host for the xfrm1 interface as follows:
- Go to Routing > Gateways and click Add.
- In Interface, select the xfrm1 interface.
- Specify the remaining gateway settings according to your network configuration.
-
Add a gateway host for the xfrm2 interface as follows:
- Go to Routing > Gateways and click Add.
- In Interface, select the xfrm2 interface.
- Specify the remaining gateway settings according to your network configuration.
Add static routes
Add two static routes with the same destination but different outbound XFRM interfaces and administrative distances. The lower the route's administrative distance, the higher its priority. So, set the administrative distance of the second route higher than the first one. This ensures the traffic continues to flow through ISP1 and fails over to ISP2 only if ISP1 goes down. When ISP1 recovers, the traffic fails back to ISP1.
To add the static routes, do as follows:
Note
The settings we use below are examples.
-
Add the first static route as follows:
- Go to Routing > Static routes and click Add.
- In Destination IP / Netmask, enter
192.168.10.0and/24 (255.255.255.0). - In Gateway, enter
10.10.10.2. - In Interface, select the
xfrm1. - In Administrative distance, enter
1.
-
Add the second static route as follows:
- Go to Routing > Static routes and click Add.
- In Destination IP / Netmask, enter
192.168.10.0and/24 (255.255.255.0). - In Gateway, enter
20.20.20.2. - In Interface, select the
xfrm2. - In Administrative distance, enter
2.
Set the route precedence
You must set the route precedence with the static route first. This ensures that the static route is prioritized over both the VPN and SD-WAN routes.
On the command-line interface, do as follows:
-
Enter 4 for Device console.
-
To set the route precedence with
staticfirst, enter the following command:system route_precedence set static vpn sdwan_policyroute -
To check the route precedence, enter the following command:
system route_precedence show
Branch office firewall
Configure the route-based VPN connections
To configure the route-based VPN connections, do as follows on your BO firewall:
-
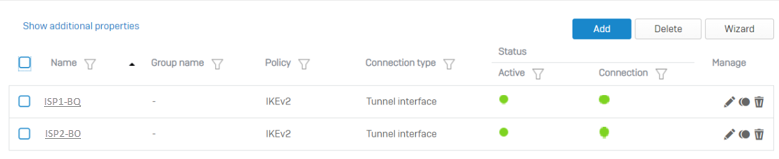
Create a route-based VPN tunnel between your HO and BO firewalls for ISP1.
-
Create a route-based VPN tunnel between your HO and BO firewalls for ISP2.
For instructions on how to create a route-based VPN tunnel, see Create a route-based VPN (any to any subnets).
To see your configured VPN connections, go to Site-to-site VPN > IPsec.
Assign IP addresses to XFRM interfaces
You must assign an IP address to each XFRM interface, as follows:
-
Go to Network > Interfaces and expand the WAN interface used to create the IPsec connection.
XFRM interfaces are automatically created for the tunnels. For example, you can see that the xfrm1 and xfrm2 interfaces are created under the WAN interface.
-
Assign an IP address to each XFRM interface.
Note
The settings we use below are examples.
- Click the xfrm1 interface.
- For IPv4/netmask, enter
10.10.10.2and/24(255.255.255.0). - Click the xfrm2 interface.
- For IPv4/netmask, enter
20.20.20.2and/24(255.255.255.0).
Add gateway hosts
Add a gateway host for each XFRM interface.
-
Add a gateway host for the xfrm1 interface as follows:
- Go to Routing > Gateways and click Add.
- In Interface, select the xfrm1 interface.
- Specify the remaining gateway settings according to your network configuration.
-
Add a gateway host for the xfrm2 interface as follows:
- Go to Routing > Gateways and click Add.
- In Interface, select the xfrm2 interface.
- Specify the remaining gateway settings according to your network configuration.
Add static routes
Add two static routes with the same destination but a different outbound XFRM interface and administrative distance. The lower the route's administrative distance, the higher its priority. So, set the administrative distance of the second route higher than the first one. This ensures the traffic continues to flow through ISP1 and fails over to ISP2 only if ISP1 goes down. When ISP1 recovers, the traffic fails back to ISP1.
To add the static routes, do as follows:
Note
The settings we use below are examples.
-
Add the first static route as follows:
- Go to Routing > Static routes and click Add.
- In Destination IP / Netmask, enter
172.16.16.0and/24 (255.255.255.0). - In Gateway, enter
10.10.10.1. - In Interface, select the
xfrm1. - In Administrative distance, enter
1.
-
Add the second static route as follows:
- Go to Routing > Static routes and click Add.
- In Destination IP / Netmask, enter
172.16.16.0and/24 (255.255.255.0). - In Gateway, enter
20.20.20.1. - In Interface, select the
xfrm2. - In Administrative distance, enter
2.
Set the route precedence
You must set the route precedence with the static route first. This ensures that the static route is prioritized over both the VPN and SD-WAN routes.
On the command-line interface, do as follows:
-
Enter 4 for Device console.
-
To set the route precedence with
staticfirst, enter the following command:system route_precedence set static vpn sdwan_policyroute -
To check the route precedence, enter the following command:
system route_precedence show