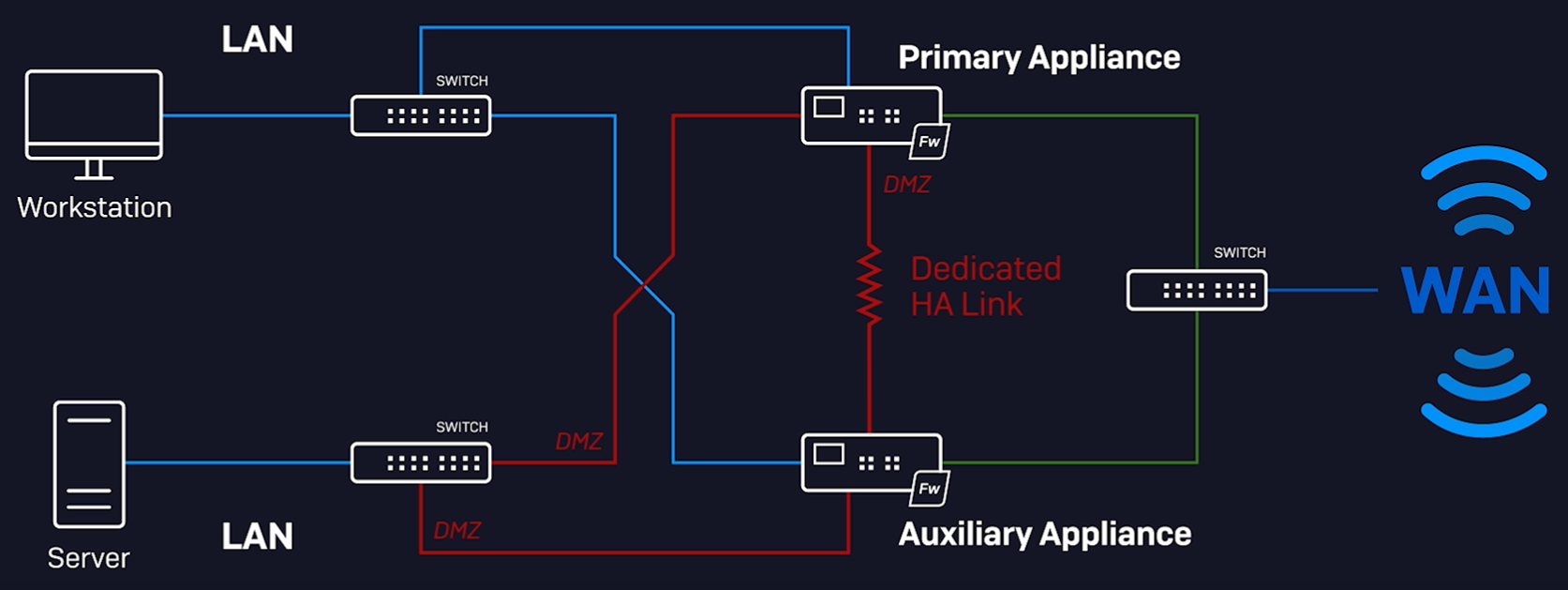
HA modes and device roles
You can configure a high availability (HA) cluster with two Sophos Firewall devices.
The two devices have a heartbeat connection, which synchronizes configuration and session details from the primary to the auxiliary device.
HA cluster
The HA cluster has a primary and an auxiliary device. A network can have more than one HA cluster. You can assign an ID to each cluster, which the firewall uses to generate virtual MAC addresses for the interfaces.
Note
If your network has multiple HA clusters, assign a different ID to each cluster to prevent virtual MAC address conflicts.
HA modes
This video shows you the HA modes and setup prerequisites.
Active-passive
In active-passive HA, the primary device processes all traffic, and the auxiliary waits as a standby device. If the primary device becomes unavailable, HA failover occurs, and the auxiliary device starts processing all traffic.
You can choose active-passive HA to ensure network resilience.
Active-active
In active-active HA, the primary and auxiliary devices share the load and process traffic. The primary device receives all network traffic and load-balances traffic with the auxiliary device. If the primary device becomes unavailable, HA failover occurs, and the auxiliary device starts processing all traffic until the primary becomes available.
You can choose active-active HA to ensure higher throughput and network resilience.
Note
Some services aren't load-balanced. See Load-balancing.
Device roles
Primary
The primary device is an active device and receives all traffic in both active-passive and active-active HA modes.
How information is synchronized and shared
-
Firewall configuration: The auxiliary device synchronizes the following information from the primary device:
-
Firewall configuration, including the rules, policies, settings, CLI commands, and the monitored port settings.
The dedicated HA link and administration ports aren't synchronized.
-
Secure storage master key and web admin console credentials. See Control center.
-
-
Active sessions: Status and details of active sessions. In active-active HA, both devices share this information with the peer.
- Heartbeat packets: Both devices share their status with the peer through the keepalive heartbeat packets.
How traffic is processed
- Only the primary device responds to ARP requests with the virtual MAC address of the responding interface. See HA traffic flow.
-
All traffic reaches the primary device.
- In active-passive HA, the primary device is active and processes all traffic.
- In active-active HA, the primary device performs load-balancing. Both devices are active and process traffic based on the load-balancing decision. See Load-balancing.
Auxiliary
The auxiliary device synchronizes its information from the primary firewall.
- Failover: In active-passive and active-active HA, the auxiliary device takes over when the primary device fails. It then becomes the primary device.
- Load-balancing: In active-active HA, the auxiliary device processes traffic along with the primary device. Requests and reply traffic reach the primary device, which takes the load-balancing decision and transfers connections to the auxiliary device.
- Administrators can access the auxiliary device's web admin console using its administrator IP address.
- In active-passive HA, Live users, DHCP lease, and IPsec live connection details don't appear on the auxiliary device's web admin console.
Initial device role
You'll choose the primary or auxiliary role for the devices when you configure HA. These are their initial roles. The role changes during failover, and the auxiliary device becomes the primary device.
When the primary device recovers after a failover, it becomes the auxiliary device. If you want it to take over as the primary device, go to System services > High availability on this device and select it under Preferred primary device.
Note
In active-passive HA mode, make sure you select the device with the licenses as Primary (active-passive) under Initial device role. See Registration and licenses.