Hardening your Sophos Firewall
See the best practices for hardening your Sophos Firewall. You must also apply these best practices to your network infrastructure, including any third-party firewalls in your network.
Keep your firmware up to date
Every SFOS update includes important security enhancements.
-
Update the firmware:
- Go to Backup & firmware > Firmware and make sure you keep your firmware up to date. See Firmware.
- Maintenance releases: Deploy every update, including all maintenance releases (MRs), because each update may include important security fixes.
-
Keep track of updates:
- Check at least once a month for firmware updates in Sophos Central or the firewall's web admin console.
- You can track the latest updates and news in the Sophos Firewall community. See Sophos Firewall community.
- Check the release notes. See Sophos Firewall release notes.
-
Schedule updates: You can easily schedule updates in Sophos Central to be applied during a period of minimal disruption to your network.
- High availability (HA): You can deploy an HA cluster. It enables you to upgrade the firmware without disruption to your network. See About high availability.
Limit access to firewall services
-
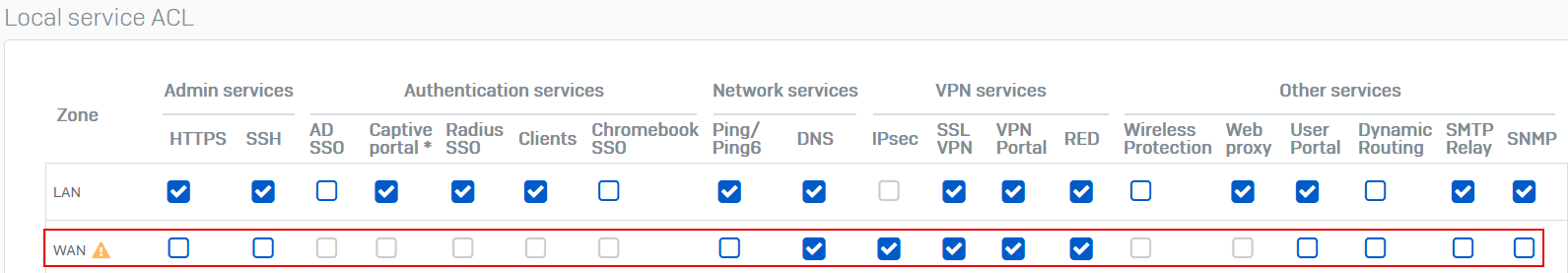
Go to Administration > Device access and make sure no services are selected for the WAN zone unless absolutely necessary.
-
Admin access:
- It's critically important that you turn off non-essential services on the WAN interface, which exposes them to the internet, particularly HTTPS (web admin console) and SSH (CLI) admin services. See Local service ACL: How device access works.
- Make sure admin interfaces are turned off or only accessible from specific trusted LAN IP addresses.
-
Don't turn on WAN access to the user portal. Instead, use VPN to access it remotely.
-
-
For remote users, consider ZTNA, which is more secure than VPN. Administrators can use ZTNA to remotely access and manage the network devices. See About Zero Trust Network Access.
-
If you use VPN, access the VPN client and configurations through the hardened, containerized VPN portal. You must turn on WAN access to the VPN portal when VPN configurations change and users need to download these configurations, or when you use Microsoft Entra ID SSO.
For more information, see the following links:
Note
Turning on WAN access for the VPN portal exposes the firewall to security risks, such as brute force attacks. To prevent security risks, see Multiple failed login attempts for WAN-facing portals on the firewall.
-
Use multi-factor authentication for all portals.
- To manage your firewall remotely, Sophos Central offers a much more secure solution, including single-sign on, than turning on WAN access to the web admin console. See Enable Sophos Central management of Sophos Firewall.
Use strong passwords, MFA, and role-based access
- Turn on Multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all administrators and users, so that they can access the portals and VPN more securely. See Multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Enforce strong passwords for all administrators and users to protect your firewall from unauthorized access gained through stolen credentials and brute force attacks.
-
Make sure your sign-in security settings are configured to block repeated unsuccessful attempts.
-
Don't turn off the CAPTCHA. It's turned on by default.
- Use role-based administrator access to limit exposure. See Device access.
Minimize access to internal systems
Any device exposed to the WAN through a NAT rule is a potential risk. If possible, don't expose any internal device, including Internet of Things (IoT) devices, to the internet through NAT or inbound connections.
- Audit and review all your NAT rules and Firewall rules regularly to make sure you don't allow unrequired WAN to LAN or remote access. See NAT rules.
- Conduct regular tests and audits of the firewall rules to spot risky configuration drifts, paying particular attention to services exposed to the WAN side of the firewall.
- Use ZTNA or VPN for remote administration and access to internal systems.
- Don't expose internal systems to the internet, especially through Remote Desktop access.
- Shut down IoT devices that don't offer a cloud proxy service and require direct access through NAT. These devices are ideal targets for attackers.
Configure appropriate protection
-
Do as follows to protect your network from exploits:
- Apply Intrusion prevention policies to firewall rules for incoming untrusted traffic.
- Go to Intrusion prevention > DoS & spoof protection and set up protection settings and policies to protect your network from DoS and DDoS attacks.
- Turn on spoof prevention and apply flags for all the DoS attack types.
See Intrusion prevention.
-
Firewall rules
- Make sure you don't have any firewall rules that allow ANY-to-ANY connections.
- Set up firewall rules to block traffic from unwanted countries and regions and regions you don't do business with. See Block countries using a firewall rule.
-
Go to Active threat response and do as follows:
- Turn on Sophos X-Ops threat feeds, and set them to Log and drop.
-
You can configure MDR threat feeds, which enable Sophos MDR analysts to push real-time threat feeds based on your network traffic related to malicious servers.
-
To monitor attacks, use Network Detection and Response (NDR) and monitor traffic to and from the firewall as well as traffic flowing through the firewall.
Turn on alerts and notifications
- Go to System services > Notification list and select the alerts and notifications of system-generated events to alert administrators. You can select email notifications and SNMP traps.
- Review the list of events, monitor the system and security events, and promptly act upon issues.
- Make sure your firewalls send logs to Sophos Central and a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solution of your choice. See Logs.