Device access
You can control access to the management services of Sophos Firewall from custom and default zones using the local service ACL (Access Control List).
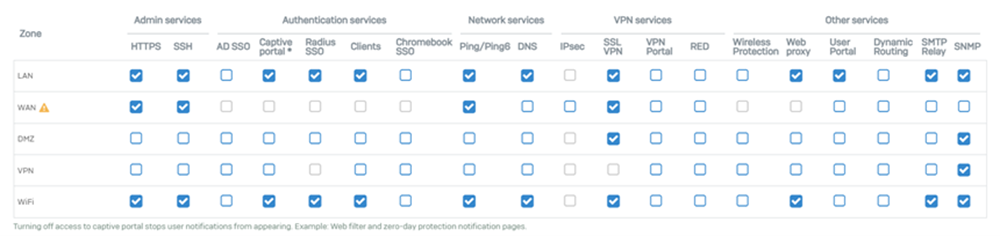
Local services are management services specific to the internal functioning of Sophos Firewall, such as web admin and CLI consoles, and authentication services. You can allow or block access to local services from Administration > Device access.
- Select the check boxes to allow access to these services from different zones. For more details about the services, go to Access to local services from zones.
- To only allow specific hosts and networks to access the services, scroll down to Local service ACL exception rule, and click Add.
Local service ACL: How device access works
The following conditions apply to local services:
- You can't control traffic to these services using firewall rules. You can only do so from Administration > Device access.
-
For custom zones, you can also allow or block access from Network > Zones.
-
To access a local service that shares a host's subnet, zone, or interface, you must select the zone. For example, to access the DNS service from the LAN zone when Sophos Firewall is the DNS server, you must select LAN for DNS.
- The default ports are used to provide access to these services, and the destination IP address is set to Sophos Firewall.
- You can change the default ports of some services, such as SSL VPN and the user portal, from the corresponding settings pages. If you change the ports, we recommend that you don't use the SSL VPN port for other services. It allows access to the services from zones that you turned off here. See SSL VPN port.
- If the firewall's web proxy is configured, the HTTP and HTTPS requests from the web proxy are internal, rather than coming from a zone, so you can't control these requests from Administration > Device access. This means users with access to the web proxy in any zone can connect to HTTP and HTTPS services, such as the web admin console, captive portal, VPN portal, and user portal, even if those services aren't turned on for the zone the users are accessing them from.
The default settings for the local service access control list are in the following image.
Default admin password settings
The factory configuration of Sophos Firewall carries a default super administrator with the following credentials:
Username: admin
Password: admin
You can use these to sign in to the web admin console and the CLI. You must change the default password when you configure Sophos Firewall for the first time. Your password must not be a commonly used password or a dictionary word. Sophos Firewall compares the password you're trying to set with a database that includes commonly used passwords and dictionary words. If your password matches a password in the database, the firewall prompts you to change it.
Sophos Firewall offers stronger password protection for the default super administrator. To benefit from the protection, you must change the password if you're upgrading from 18.0 MR3 or earlier or 17.5 MR14. This is a one-time change.
You can't rename or delete the default administrator account.
Note
Store the current password in a secure location. If you move to an earlier firmware version that uses the current password, you'll need it to sign in.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) for default admin
You can set up MFA based on hardware or software tokens for the default administrator.
- Turn on MFA for default admin and click Apply.
-
Select a token method and click Next:
-
Configure a hardware token:
- Enter the key the device manufacturer provides.
- Enter the timestep that matches the value configured in the hardware token.
-
Click Next and enter the default admin's password followed by the passcode shown on the hardware token.
Example:
<password><passcode> -
Click Validate and click Apply.
-
Generate a software token:
- Install an authenticator app on your mobile device and scan the QR code.
- Enter your password followed by the passcode in the following format:
<password><passcode>. - Click Validate and click Apply.
Warning
If you apply MFA for the default admin, make sure you store the additional passcodes in a secure location, such as a password manager. See Generate passcodes on the firewall.
If you don't, you risk losing access if the default admin loses the mobile device that has the authenticator app.
Note
If the hardware or software token isn't available, you can skip MFA the next time the default administrator signs in to the web admin console, or you can reset the MFA. See Skip multi-factor authentication for next admin user login or Reset multi-factor authentication for Admin user.
-
If you have an existing hardware or software token and are only turning on MFA, choose from the following options and follow the instructions:
- Use an existing token: Enter the password followed by the passcode.
- Generate a software token: Scan the QR code using an authenticator app.
Public key authentication for admin
Administrators can gain secure access to the CLI using private keys instead of passwords. Public-private key pairs deliver encrypted communication and enhanced security.
Learn how to generate a public-private key pair, add the public key to the firewall, and turn on public key authentication for administrators to access the CLI.
Supported SSH keys
The firewall supports the following SSH key types:
- RSA keys with a minimum size of 2048 bits
- DSA keys with a minimum size of 2048 bits
- ECDSA keys excluding the ED25519 algorithm
Generate a public-private key pair
To generate a key pair, do as follows:
- Use an SSH tool, such as PuTTYgen, and generate a public-private key pair.
-
Copy the public key.
You must paste it in the firewall later.
-
Download the private key file.
- Share the private key file with the administrator who needs secure access to the CLI.
Add the public key to the firewall
To allow secure access to the CLI using the SSH key, do as follows:
- Go to Administration > Device access, scroll down to Public key authentication for admin, and turn on Enable authentication.
-
Under Authorized keys, paste the public key and click the plus button.
-
Click Apply.
The Apply button doesn't appear to custom administrators.
Administrators must enter the private key in the SSH tool they use, for example, PuTTY.